If you’ve visited a doctor lately, you may have experienced how your healthcare data — records, scans, prescriptions — is increasingly accessible wherever you interact with a healthcare provider. But you don’t control your own healthcare data storage. Enter cloud-based solutions.
Although still immature, cloud-based healthcare data storage is an emerging solution with potential to become a market disruptor, according to Gartner Emergence Cycle research.
Download eBook: 3 Steps for a Winning Product Strategy
This and other emerging cloud-based technologies are exactly what adventurous technology product leaders are looking for: opportunities to gain competitive advantage by identifying key innovations early. Gartner maps them on its Emergence Cycle for Cloud-Based Technologies.
Cloud-based healthcare data storage
Electronic health-related records increasingly exist everywhere that patients and customers interact, from doctors’ offices to hospitals and pharmacies and even wearable devices. But individuals don’t own and control the single source of truth for their own healthcare data.
That control currently lies with the providers that enter the data — device manufacturers, hospitals, medical practices and pharmacies, which store data for their own exclusive purposes.
Cloud-based solutions for healthcare data storage would allow individuals to own and control the single source of truth for their health and medical data, which they could choose to share with providers, granting them permission to add or retrieve data as needed.
To date, the limitations on individually empowered healthcare data storage and use include:
- Systems aren’t integrated — and achieving integration will likely be the primary hurdle.
- Data and data models are proprietary and fiercely guarded, often in electronic health record (EHR) systems.
- Individuals have very limited visibility into the data and how it’s used, except perhaps the data captured by personal wearable devices.
Strategy for technology providers
Technology providers can improve the success of healthcare data storage and related applications and solutions by partnering to improve the credibility of such ventures.
If you’re a tech product provider in the healthcare field, look for a partner capable of delivering and taking to market a solution that can meet the integration and scalability challenges this technology presents. If you’re a technology expert, find a partner with a deep understanding of health-related consumer and business challenges, particularly one with the vision to see the potential of the very different industry landscape this technology will create.
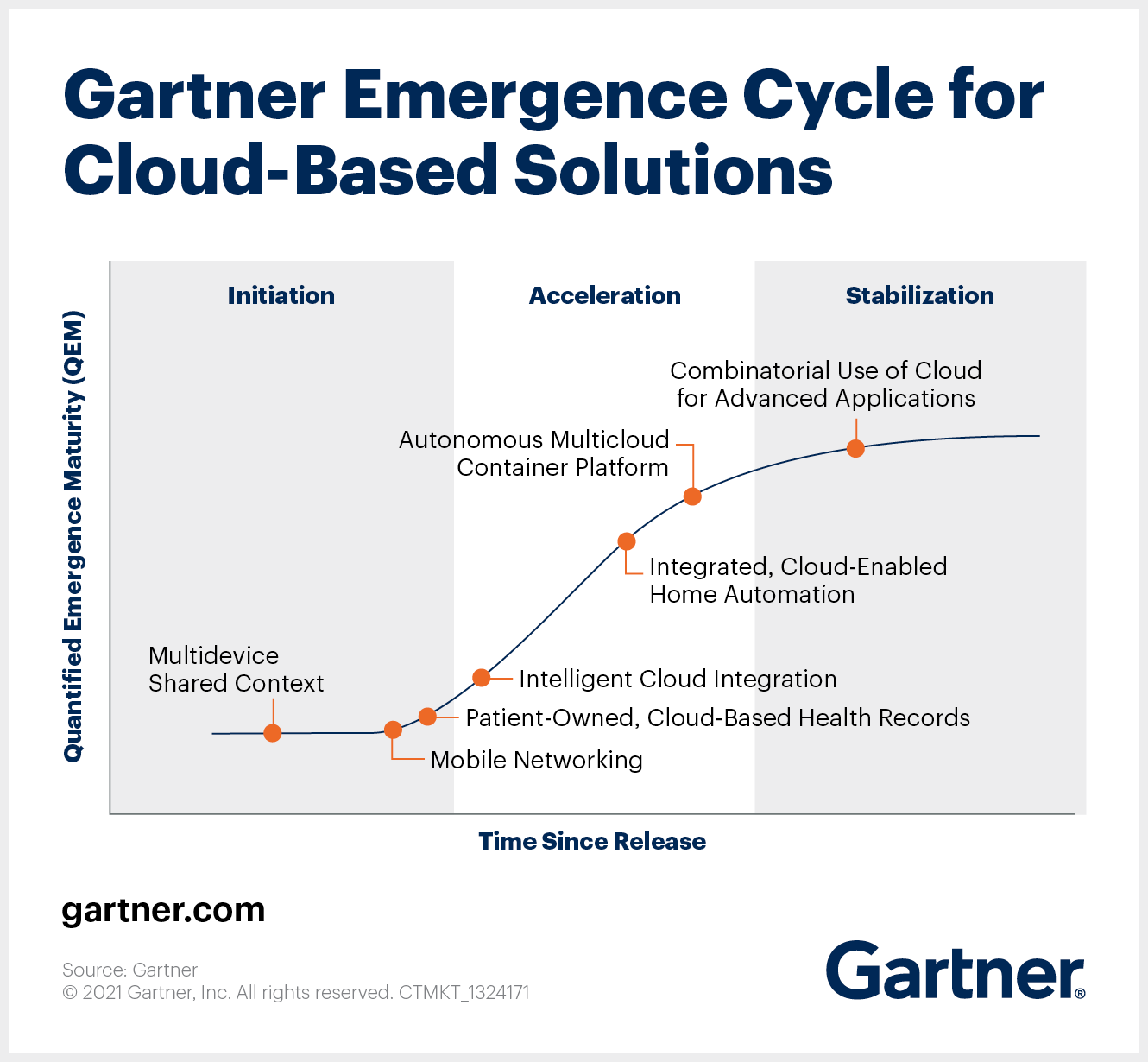
Gartner Emergence Cycle for Cloud-Based Technologies
Health records are only one of the innovations on the Gartner Emergence Cycle for Cloud-Based Technologies. The cycle offers a glimpse into a range of technologies and application models that may be little more than patent applications and academic papers today, but have the potential to be market disruptors tomorrow.
Emerging technologies are exciting because of the promise of new capabilities and first-mover advantages. Some technology providers patiently wait for these technologies to mature before they adopt them, as they feel that their customers prefer stable products with proven technologies over the “bleeding edge.”
Others jump on the chance to be early adopters, even if the technology is immature. For some, the potential improvements and competitive advantages are so enticing that they seek technologies that have not yet been brought to market.
The Gartner Emergence Cycle uses a rough index of time versus maturity. Technologies often start slowly, with limited activity around patents and papers. Eventually, some accelerate as researchers and technology providers start to see their potential. Finally, the maturity stabilizes as the technology becomes ready for the market.
Technology providers can make the best use of the Gartner Emergence Cycle by taking inspiration from its profiles. For the technologies, consider how it could change your product’s capabilities or delivery mechanisms. For the application models, consider the opportunities such models could present for your business or how a similar model could work in your own market.
Read more: 6 Key Forces Shaping Technology and Service Providers Through 2025 Trends Impact Radar for 2021
Cloud-based mobile networking and container platforms
“Cloud” is a broad topic, and the emergence cycle covers application models that leverage the cloud (like patient-owned cloud-based health records) and technologies that enable cloud-based applications, such as cloud-based mobile networking and container platforms — all at varying degrees of maturity.
Cloud-based mobile networking
Mobile networking is commonly understood to be the networking capabilities of mobile devices, and is generally associated with cellular mobile services. However, mobile networking must evolve beyond the fixed mobile networks in use today to a dynamic, responsive and intelligent model of interconnection between mobile systems of all types.
Next-generation mobile networking must account for the ability of individual entities, including digital entities, to dynamically discover, connect, interact and disconnect in an ad hoc fashion.
Connections must extend beyond peer-to-peer connections and include multidevice networking. Mobile networking must evolve to support both the increasing mobility of digital entities as well as the random and unpredictable interactions among entities. Spontaneous and multidevice mobile networking will provide devices a means to connect, share information and disconnect to provide a deeper, and in many cases, shared, context for rapidly evolving scenarios.
Cloud-based mobile networking is still squarely in the initiation phase, but technology providers can architect systems for dynamic interoperability by incorporating multifaceted mobile networking solutions. Building next-generation digital solutions that incorporate contextual insight means leveraging multidevice mobile networking to spontaneously and securely connect and share information between devices and other mobile entities.
To support these capabilities, tech providers need to establish competencies in advanced mobile networking technologies associated with digital twins, mobile devices, cellular-assisted proximity-based connectivity and other advanced mobile networking solutions.
Autonomous multicloud container platform
Today’s container platforms are basically siloed by cloud and can only provide very basic centralized management capabilities in multicloud environments. This is far from supporting “autonomous multicloud,” an advanced form of multicloud. With autonomous multicloud, the workload’s components and services are distributed and highly automated among multiple cloud providers.
The “autonomous multicloud container platform” will enable consistent multicloud implementation, not only through centralized management but also consistent infrastructure-backing services and application deployment capability. One possible implementation is a serverless container platform that spans multiple public clouds and eliminates the need for users to provision aspects of the infrastructure to run the containers.
Technology providers should prioritize the selection and development of consistent infrastructure-backing services and application deployment services in a multicloud environment. Examples include multicloud data services and continuous integration/continuous delivery (CI/CD) services that can run on container platforms, unified monitoring, single sign-on access and authentication, policy enforcement, and integrated backup and disaster recovery.
![]()
The post Healthcare Data Storage and Other Innovations Head to the Cloud appeared first on Smarter With Gartner.